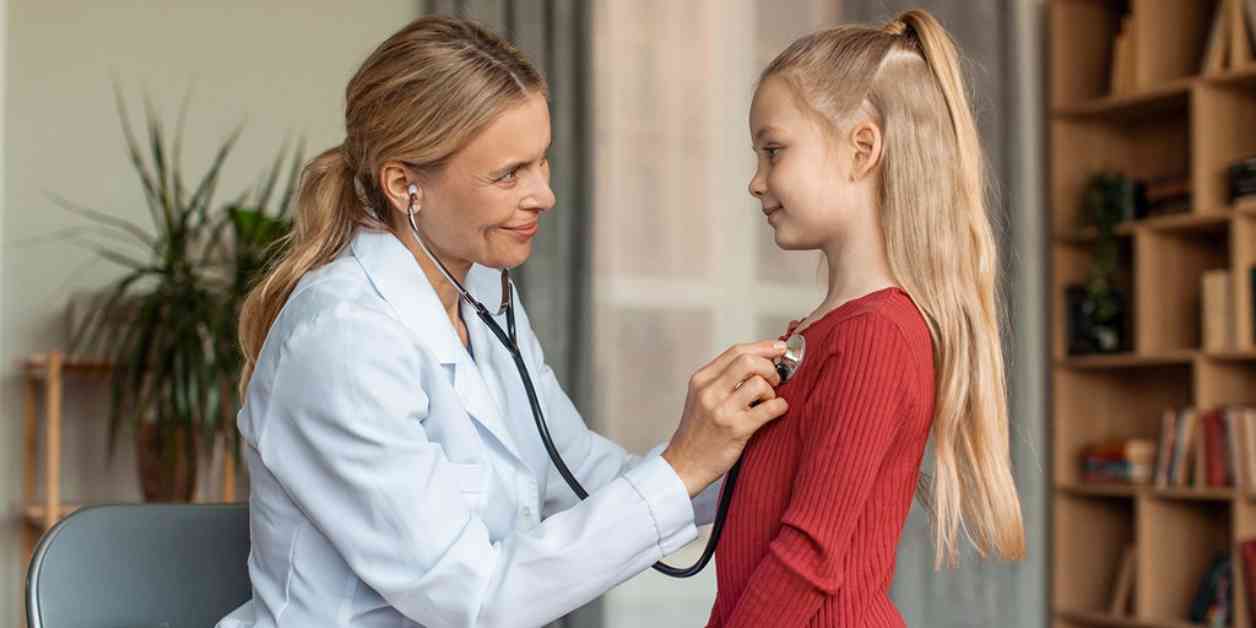New research from the American Heart Association (AHA) has shed light on the concerning prevalence of high blood pressure among children and teens in the United States. According to the preliminary findings, about 14% of youths in the U.S. have high blood pressure or are at risk of developing it. This revelation underscores the importance of monitoring and addressing this issue early on, as hypertension can lead to serious health complications later in life, such as heart attack and stroke.
Study Details
Lead researcher Dr. Ahlia Sekkarie and her team delved into the blood pressure and body mass index (BMI) data of 2,600 children and teens aged 8 to 19. The data was collected from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey spanning from 2017 to 2020. The researchers found that 8.7% of youths had elevated blood pressure, while 5.4% had high blood pressure or hypertension.
Interestingly, the study revealed that boys had higher blood pressure measurements compared to girls, and blood pressure levels tended to increase with age. Furthermore, the prevalence of high blood pressure was more pronounced among individuals with severe obesity. It was noted that Hispanic youths had the lowest rate of elevated blood pressure, highlighting potential disparities in health outcomes among different demographic groups.
Implications and Recommendations
Dr. Sekkarie emphasized the importance of addressing high blood pressure in childhood, as it serves as a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke in adulthood. Early intervention and the adoption of healthy habits during childhood can help reduce the likelihood of developing cardiovascular issues later in life. This underscores the critical role that parents and caregivers play in promoting a healthy lifestyle for children.
While the study did not delve into the specific reasons behind the high rates of pediatric hypertension, Dr. Sekkarie suggested that obesity could be a major contributing factor. Given that approximately one in five children in the U.S. is affected by obesity, it is crucial to prioritize measures that promote healthy weight management and overall well-being in young individuals.
Preventive Measures
The American Heart Association recommends several strategies to manage and prevent high blood pressure in children and teens. These include maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a nutritious diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and limiting intake of saturated fats. Additionally, reducing sodium and alcohol consumption, avoiding smoking, and staying physically active are crucial components of regulating blood pressure and promoting cardiovascular health.
Dr. Bradley Serwer, a cardiologist and chief medical officer at VitalSolution, emphasized the importance of early screening for blood pressure and cholesterol levels in young individuals. Identifying and addressing potential risk factors early on can help mitigate the long-term consequences of cardiovascular issues. Dr. Serwer underscored the significance of dietary modifications, particularly reducing sodium intake, as a primary approach to managing borderline or high blood pressure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the findings from the American Heart Association study serve as a wake-up call for parents, healthcare providers, and policymakers to prioritize the monitoring and management of high blood pressure in children and teens. By instilling healthy habits early on and promoting a supportive environment for maintaining cardiovascular health, we can empower the younger generation to lead healthier lives and reduce the burden of heart disease and stroke in the future. It is imperative that we take proactive steps to address this issue and prioritize the well-being of our youth for a healthier tomorrow.