Identifying Early Signs of Prostate Cancer: Symptoms and Warning Signs
Prostate cancer is a prevalent disease among men, with one in eight men being diagnosed in their lifetime, according to the American Cancer Society. It is the second most common cancer diagnosed in men, following skin cancer. Despite its prevalence, symptoms of prostate cancer are often minimal or nonexistent, making early detection challenging.
### Understanding Prostate Cancer
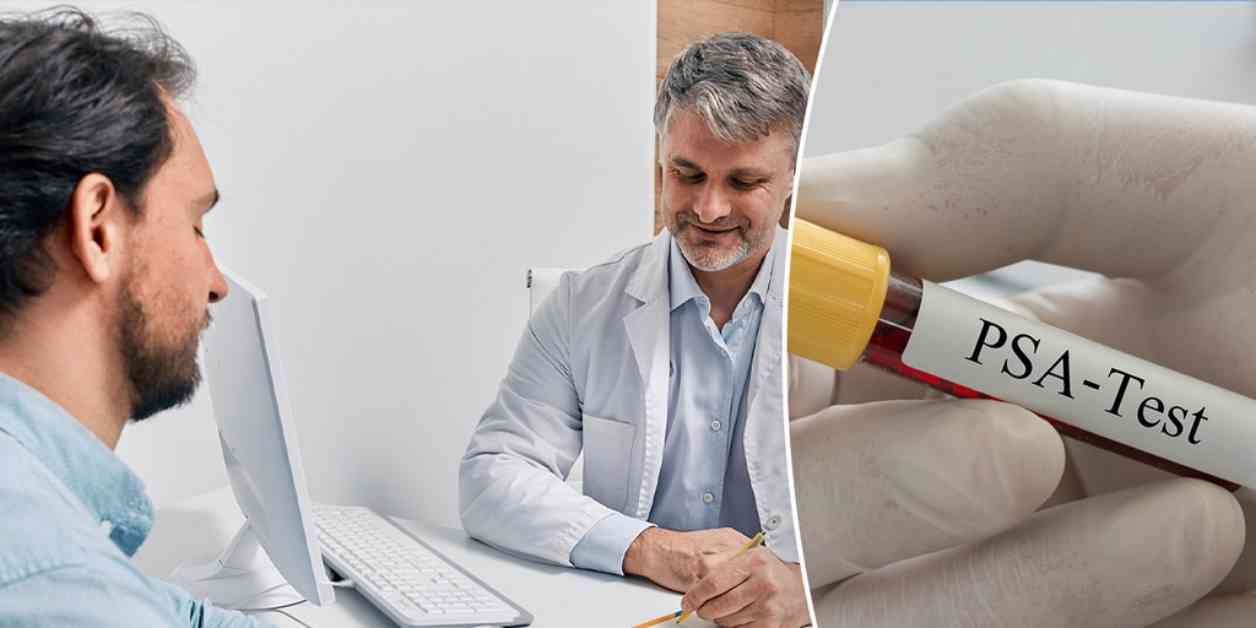
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland in men, with the potential to spread to other areas of the body. The most common way to screen for prostate cancer is through a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. This type of cancer can grow slowly, and many individuals may not experience any symptoms at all.
### Recognizing Symptoms and Risk Factors
Symptoms of prostate cancer may include pain in the bones and weight loss, especially in advanced stages when the cancer has spread. However, most men with prostate cancer do not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. Risk factors for developing prostate cancer include age, with men between 60 and 74 being at higher risk, as well as family history of the disease. Men of African, Afro-Caribbean, South Asian, and Hispanic descent are also more susceptible to aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
### Types of Prostate Cancer and Treatment Options
The most common type of prostate cancer is adenocarcinoma, which originates in the gland cells. Other rare types include small cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors, transitional cell carcinomas, and sarcomas. Prostate cancer is curable, especially when diagnosed early. Treatment options vary depending on the cancer’s stage and the individual’s overall health, with options ranging from active surveillance to radiation or surgery.
### Importance of PSA Screening
PSA screening has been a topic of debate, with recommendations varying over the years. While the U.S. Preventative Services Task Force has advised against routine PSA screening in the past, recent guidelines suggest that men between 55 and 69 should discuss the benefits and risks with their physicians. PSA screening can potentially reduce the risk of death from prostate cancer, but false-positive results and overdiagnosis are possible complications to consider.
In conclusion, early detection and regular screenings are crucial in identifying prostate cancer in its early stages. Men should consult with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action based on individual risk factors and preferences. Stay informed and proactive in managing your health to reduce the impact of prostate cancer.