Could Recess and Incentives Keep Kids in School?
Chronic absenteeism has been a longstanding issue in American schools, but the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the problem, leading to even higher rates of students missing school. According to data collected by The Associated Press and Stanford University economist Thomas Dee, roughly one in four students in the 2022-23 school year remained chronically absent, meaning they missed at least 10% of the school year. This represents about 12 million children in the 42 states and Washington, D.C., where data is available. Before the pandemic, only 15% of students missed that much school.
The effects of pandemic school closures are still being felt in schools across the country. After spending as much as a year at home, many students have found the transition back to in-person learning overwhelming, boring, or socially stressful. As a result, both kids and parents have become more accepting of staying home, making it even harder for schools to address the issue of chronic absenteeism.
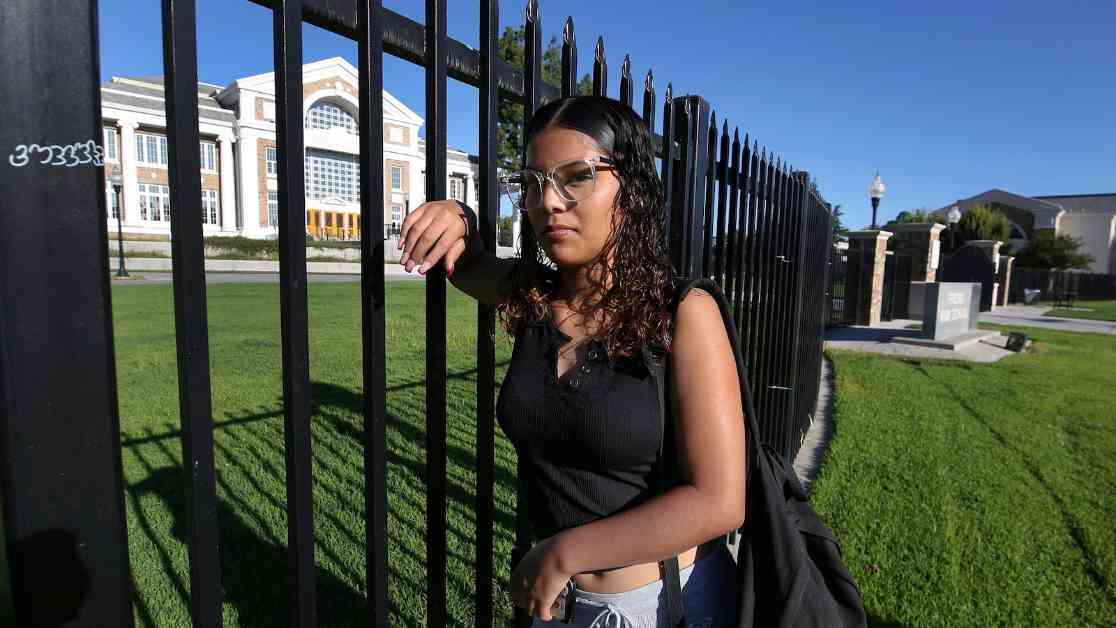
However, schools are beginning to implement creative solutions to improve attendance rates among students. One innovative approach taken by Medford High School in Massachusetts involved offering students the opportunity to participate in organized sports during lunch if they attended all their classes. This initiative, akin to providing high schoolers with recess, proved to be a success, with students like Flerentin “Flex” Jean-Baptiste experiencing a significant reduction in absences. The school saw a decrease in chronic absenteeism from 35% in March 2023 to 23% in March 2024, marking one of the most substantial declines among Massachusetts high schools.
Subheadings:
1. The Impact of COVID-19 on School Attendance
2. Creative Solutions to Address Chronic Absenteeism
3. The Importance of Supportive Teachers and Mentors
The Impact of COVID-19 on School Attendance
The disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have had far-reaching consequences on the education system, with attendance rates taking a significant hit. Nearly every state is still grappling with attendance issues, as students continue to miss school at alarming rates. The lingering effects of the pandemic, coupled with ongoing challenges such as financial hardship, transportation issues, and mental health struggles, have contributed to the persistent problem of chronic absenteeism.
In Oakland, California, chronic absenteeism soared from 29% pre-pandemic to 53% in the 2022-23 school year. To address this issue, the district implemented a grant-funded program that incentivized students to attend school regularly. The program offered monetary rewards for perfect attendance, along with daily check-ins with an assigned adult and weekly mental health assessments. While paying students may not be a long-term solution, it proved effective in improving attendance rates and addressing the underlying issues that prevented students from coming to school.
Creative Solutions to Address Chronic Absenteeism
Schools across the country are exploring innovative strategies to combat chronic absenteeism and foster a culture of regular attendance among students. In Medford High School, Principal Marta Cabral introduced lunchtime gym sessions as a way to incentivize students to attend all their classes. This initiative not only provided students with a much-needed break but also gave them something to look forward to during the school day.
Similarly, in Fresno, California, Fort Miller Middle School took a proactive approach to address the root causes of chronic absenteeism. By providing families with access to a washer and dryer and offering transportation services for students who missed the bus, the school was able to improve attendance rates significantly. These efforts underscore the importance of addressing the practical barriers that prevent students from attending school regularly.
The Importance of Supportive Teachers and Mentors
In addition to implementing structural changes within schools, the role of supportive teachers and mentors cannot be understated in addressing chronic absenteeism. For students like Golden Tachiquin, who struggled with anxiety and missed school frequently, having a teacher who understood her culturally and provided emotional support made a world of difference. Tachiquin’s experience highlights the importance of building strong relationships between students and educators to create a sense of belonging and support.
Research has shown that students who identify with their teachers are more likely to attend school regularly. Programs like Oakland’s African American Male Achievement project, which pairs Black students with Black teachers for additional support, have been instrumental in improving attendance rates and fostering a sense of community within schools. By prioritizing mentorship and personalized support, schools can help students overcome barriers to attendance and succeed academically.
In conclusion, chronic absenteeism remains a pressing issue in American schools, exacerbated by the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, schools are taking proactive steps to address this problem by implementing creative solutions, fostering supportive relationships between students and educators, and providing incentives for regular attendance. By prioritizing student well-being and creating a conducive learning environment, schools can empower students to overcome barriers to attendance and thrive academically.