Understanding the Impact of Unpaid Medical Bills on Patients
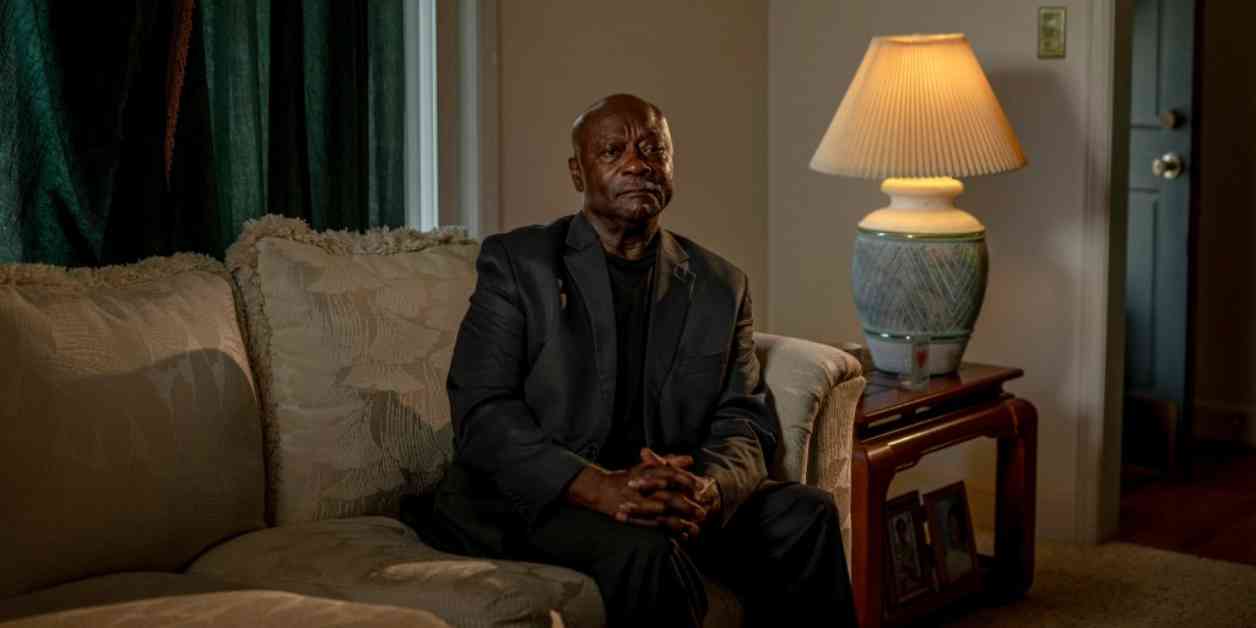
Terry Belk, a 68-year-old man from North Carolina, has been battling medical debt for over 20 years. He describes it as an albatross around his neck, a burden that he carries every day. Belk’s situation is not unique, as Americans collectively owe at least $220 billion in medical debt. According to KFF, a nonprofit health policy research organization, South Dakota, Mississippi, and North Carolina are among the top states with the highest percentage of residents affected by medical debt.
Medical debt is a significant issue that affects millions of Americans, leading to financial anxiety and even bankruptcy in some cases. The rising costs of healthcare in the United States make it challenging for individuals to afford necessary medical treatments. Despite the implementation of the Affordable Care Act, which requires nonprofit hospitals to offer financial assistance programs to patients in need, many people still struggle to pay their medical bills.
The Challenges of Managing Medical Debt
One of the major challenges faced by patients dealing with medical debt is the lack of transparency in billing practices. Hospital bills are often complicated and difficult to decipher, leading to confusion and frustration among patients. Cynthia Fisher, founder of PatientRightsAdvocate.org, highlights the issue of incorrect billing, noting that many patients receive bills that do not accurately reflect the services they received.
In addition to inaccurate billing, the cost of healthcare services can vary significantly from one hospital to another. A study by PatientRightsAdvocate.org found that prices for common procedures such as appendectomies, cesarean sections, and cataract surgeries can differ greatly within the same facility. This variability in pricing makes it challenging for patients to understand the true cost of their care and can lead to unexpected financial burdens.
The Impact of High Medical Debt on Patients
Darcy Guill, a 52-year-old woman from North Carolina, experienced firsthand the challenges of managing medical debt. After undergoing emergency hernia surgery, she received a $4,000 bill from the hospital for expenses not covered by her insurance plan. Guill, who lives in a rural community and has multiple sclerosis, is now making monthly payments to chip away at her debt.
The financial strain of medical debt can be particularly severe for individuals living in states with limited access to healthcare services. Residents of southeastern states, where Medicaid expansion has been restricted, often face higher levels of medical debt due to the lack of affordable insurance options. North Carolina, in particular, has seen a rise in medical debt among its residents, with recent mergers among hospitals contributing to higher healthcare costs.
In North Carolina, hospitals have the legal authority to sue patients for unpaid medical bills, with judgments lasting up to 20 years and carrying 8% interest rates. These legal actions can have severe consequences for patients, potentially resulting in liens against their homes and further financial hardship.
Overall, the issue of unpaid medical bills is a complex and challenging problem that requires attention and action to ensure that all individuals have access to affordable healthcare. Through increased transparency in billing practices, improved access to financial assistance programs, and policy changes to address rising healthcare costs, we can work towards alleviating the burden of medical debt on patients across the country.