Maximize Your Workout Gains with Improved Grip Strength
As you strive to push your limits and reach new levels of fitness, it’s crucial to pay attention to even the smallest details that can make a significant impact on your progress. One often-overlooked factor that can greatly enhance your workout gains is grip strength. In this Quick Training Tip, we’ll delve into the importance of grip strength in your training regimen and how you can leverage different grip orientations to optimize your workouts.
The Role of Grip Strength in Weightlifting
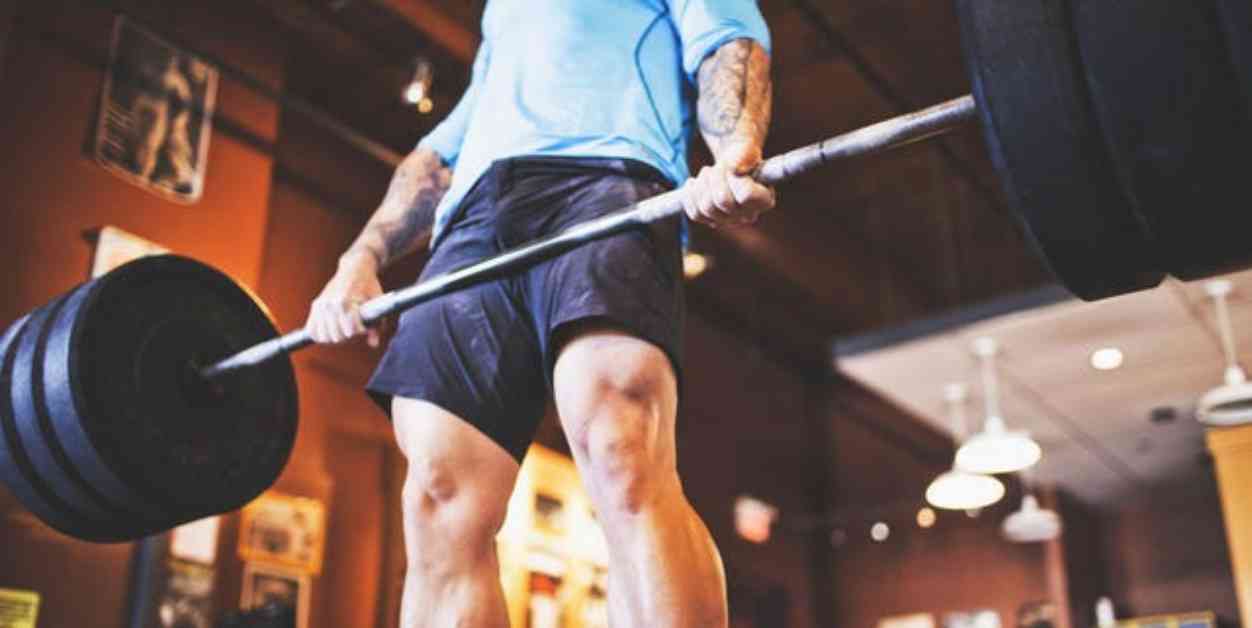
When it comes to weightlifting, grip strength plays a crucial role in your ability to perform exercises effectively and efficiently. Whether you’re lifting weights, performing bodyweight exercises, or using specialty equipment, your grip strength directly impacts your performance. A strong grip not only allows you to maintain proper form and stability during lifts but also enables you to lift heavier weights and target specific muscle groups more effectively.
Different Types of Strength Training Grips
There are various grip orientations that you can utilize in your training to target different muscle groups and enhance your overall performance. Understanding the different types of grips and their applications can help you maximize your workout gains and avoid plateaus in your training progress.
1. Pronated (Overhand) Grip: This grip involves positioning your palms facing down, which is commonly used in exercises like pull-ups and strict deadlifts. The pronated grip primarily targets your back muscles and forearms, making it ideal for exercises that require pulling movements.
2. Supinated (Underhand) Grip: In contrast, the supinated grip involves positioning your palms facing up, commonly used in exercises like chin-ups and bicep curls. This grip places more emphasis on the biceps and can help you isolate and develop these muscles effectively.
3. Alternated or Mixed Grip: The alternated or mixed grip involves using one hand in a pronated position and the other in a supinated position, often used in heavy deadlifts to improve grip strength and stability.
4. Neutral Grip: The neutral grip involves positioning your palms facing each other, such as in hammer curls. This grip helps target different muscle groups and can provide added stability during exercises.
5. Hook Grip: The hook grip involves “hooking” your thumb between the bar and wrapping your fingers around it, providing a secure hold for heavier lifts. This grip is commonly used by advanced lifters to support heavy weights and prevent grip fatigue.
The Impact of Grip Orientation on Muscle Recruitment
The orientation of your grip during exercises can have a significant impact on which muscle groups are targeted and activated. By adjusting your grip position, you can effectively shift the focus of the exercise and engage different muscles to achieve optimal results.
For example, in a dumbbell curl, using a standard supinated grip primarily targets the biceps. However, by rotating your hands to a neutral grip, you can shift the emphasis to the brachialis, another elbow flexor muscle. Rotating your hands to a pronated grip will target yet another elbow flexor, the brachioradialis, allowing you to diversify your training and stimulate different muscle groups effectively.
Additionally, grip orientation can impact the security and stability of your lifts, especially as you progress to heavier weights. In compound lifts like the barbell deadlift, a strong grip is essential to prevent grip failure and ensure the safety and effectiveness of the exercise. By choosing the right grip orientation, such as a hook or mixed grip, you can support heavier weights and maximize your strength gains without compromising your form.
Choosing the Right Grip for Your Workouts
When selecting a grip for your exercises, consider the specific muscle groups you want to target and the type of movement you’re performing. Different grips offer unique benefits and can help you achieve specific training goals more effectively.
For example, in the barbell bent-over row, using a pronated grip targets the back muscles, while switching to a supinated grip engages the biceps more. By incorporating different grips into your workouts, you can diversify your training and maximize muscle recruitment to achieve optimal results.
If you’ve been struggling to make progress in certain exercises, consider changing your grip orientation to challenge your muscles in new ways. By incorporating variations like pull-ups, chin-ups, hammer curls, and reverse grip rows, you can stimulate different muscle groups and break through training plateaus to achieve new levels of strength and performance.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, grip strength is a critical component of your training regimen that can significantly impact your workout gains and overall performance. By understanding the different types of grip orientations and their applications, you can optimize your training, target specific muscle groups, and enhance your strength gains effectively.
Remember to experiment with different grip positions in your workouts, monitor your progress, and adjust your training approach as needed to continue making strides in your fitness journey. With a solid understanding of grip strength and its importance in weightlifting, you can maximize your workout gains and elevate your training to new heights.