Obesity Rates in US Stabilize, Severe Obesity on the Rise: CDC Report
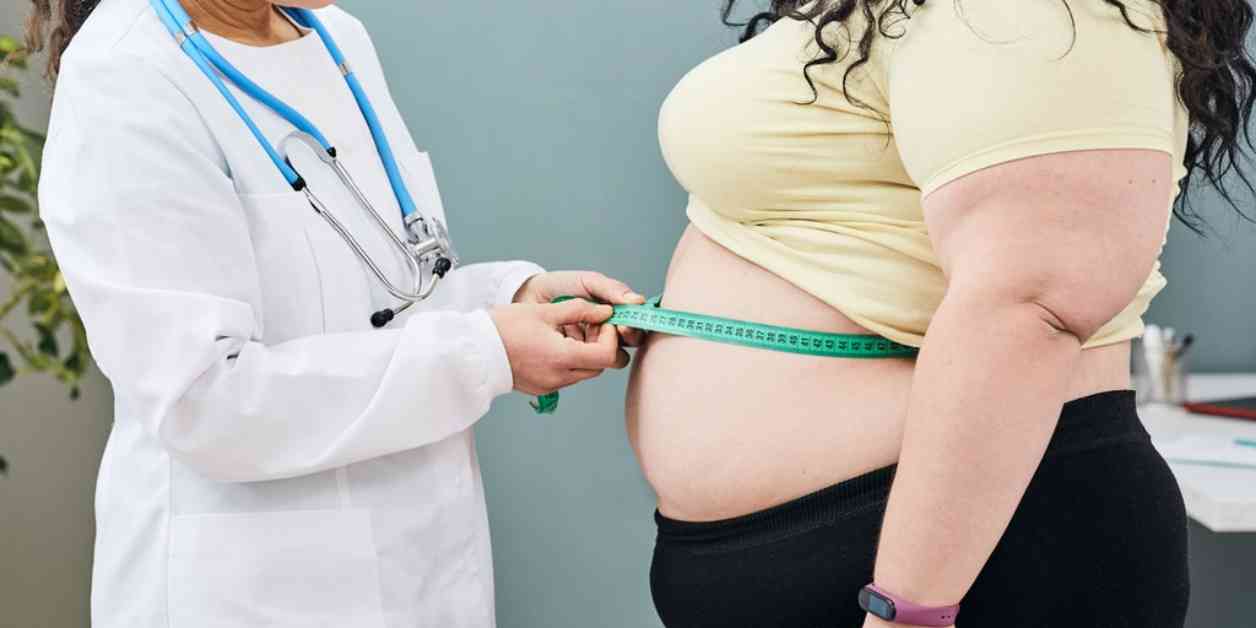
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently released a report highlighting the current state of obesity in the United States. While the overall rate of obesity among adults has remained stable, there has been a concerning increase in the rate of severe obesity.
According to the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics, the rate of obesity among adults in the United States was approximately 40.3% between August 2021 and August 2023. This marks a slight decrease from the 41.9% rate of obesity reported in 2020. However, despite this small decline, the prevalence of severe obesity continues to rise.
Steady Decline in General Obesity Rates
In recent years, general obesity rates have either slowed down or slightly decreased. This shift represents a departure from the consistent upward trend seen in previous years. While the decline in obesity rates may not be significant enough to reverse the epidemic on a national scale, it does signal a potential turning point in the fight against obesity.
Since 2011, reports from the CDC have shown a steady increase in the number of U.S. adults struggling with obesity. While the current stabilization of general obesity rates is a positive development, it is crucial to address the underlying factors contributing to the ongoing obesity crisis in the country.
Rise in Severe Obesity Despite Overall Trends
Despite the slowdown in general obesity rates, the prevalence of severe obesity continues to climb. The CDC’s report indicates that the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity increased from 7.7% to 9.7% between 2013–2014 and August 2021–August 2023. This upward trajectory highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions to address severe obesity in the population.
Individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher are classified as obese, while those with a BMI of 40 or higher fall into the category of severe obesity. The gender disparities in severe obesity are also notable, with men exhibiting a lower prevalence (6.7%) compared to women (12.1%). The prevalence of severe obesity was highest among men aged 40–59 and women aged 20–39 and 40–59.
Public Health Initiatives and Long-Term Goals
The CDC’s national “Healthy People 2030” plan outlines ambitious goals to promote healthy eating and physical activity to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. One of the key objectives of this initiative is to reduce the rate of obesity to below 38.6% by 2030. However, the CDC has acknowledged that the obesity crisis is only worsening, underscoring the need for comprehensive strategies to combat this pervasive public health issue.
As policymakers and healthcare providers work towards addressing the complex factors contributing to obesity, it is essential to prioritize evidence-based interventions that target both general and severe obesity. By fostering a supportive environment that promotes healthy lifestyles and sustainable weight management, it is possible to make meaningful progress in curbing the obesity epidemic in the United States.
In conclusion, while the overall rate of obesity in the United States has stabilized, the prevalence of severe obesity continues to rise. This dual trend underscores the pressing need for targeted interventions and public health initiatives to address obesity at both the individual and population levels. By implementing comprehensive strategies that promote healthy behaviors and empower individuals to make positive choices, we can work towards reducing the burden of obesity and improving the overall health and well-being of our communities.