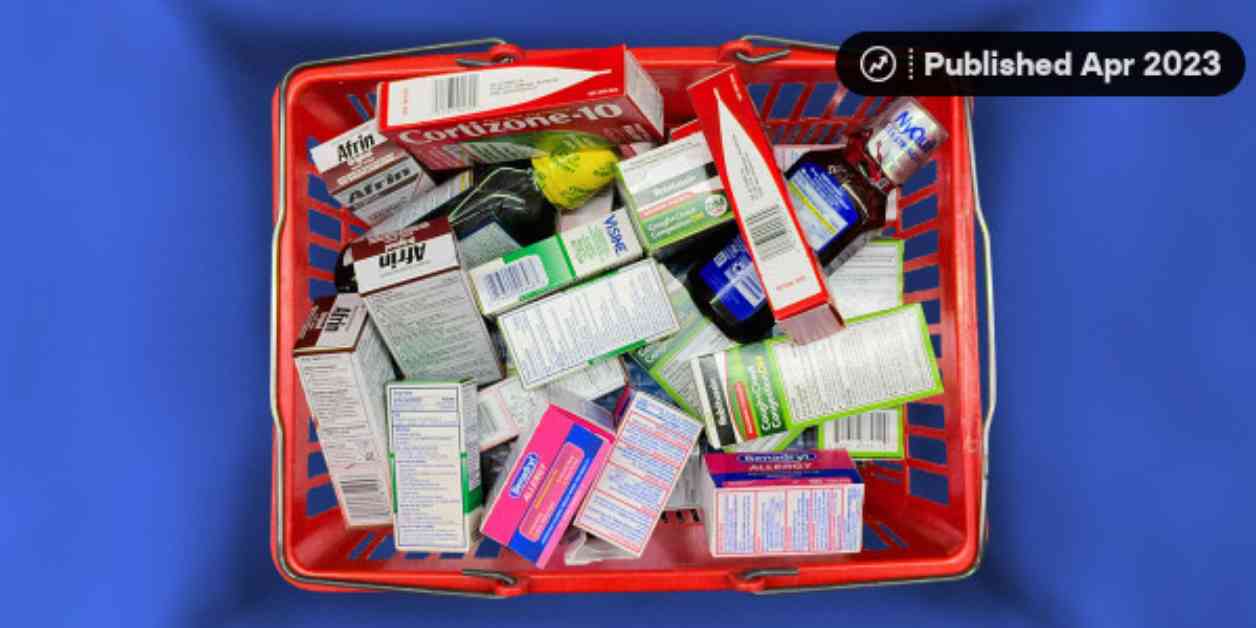
Over-The-Counter Drugs: The Potential for Addiction
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are a convenient and accessible way to treat various common ailments without the need for a prescription. However, what many people may not realize is that some of these seemingly harmless drugs have the potential to lead to addiction if not used correctly. George Resch, popularly known as TankSinatra on social media, recently shared his experience with addiction to the over-the-counter nasal spray Afrin. On a podcast called Meme Daddies, he opened up about his year-long struggle with congestion and how it led to dependency on the nasal spray.
The Risk of Misuse and Dependency
Misusing OTC medications can have serious consequences, including the development of physical dependency on the drug. This means that the body becomes reliant on the substance to function normally, even if it was initially used to treat a specific condition or symptom. While dependency is not the same as addiction, it can still have harmful effects on the body.
Dr. Kelly Johnson-Arbor, a medical toxicologist, explains that addiction involves compulsive behavior to obtain the drug despite negative consequences. This can occur with substances like fentanyl, oxycodone, or illicit drugs such as cocaine or heroin. Individuals with addiction often require increasing amounts of the substance to achieve the desired effects, leading to a cycle of misuse and dependence.
Understanding the Rebound Effect
One common issue that arises from the misuse of OTC medications is the rebound effect. This occurs when the original symptoms that the drug was meant to alleviate return, sometimes even more severe than before, once the drug is discontinued. It is essential to follow the label instructions and use these medications for short periods as directed to avoid the rebound effect.
Pat Aussem, an associate vice president of consumer clinical content development, highlights that misuse can occur when individuals exceed the recommended dosage, use the drug for longer than advised, or use it for purposes other than intended. This can lead to unpleasant physical consequences, withdrawal symptoms, and even addiction in some cases.
Common OTC Drugs with Addiction Potential
1. **Nasal Sprays with Oxymetazoline**: Afrin, a popular nasal decongestant, contains oxymetazoline, which can lead to a condition known as rhinitis medicamentosa if used for prolonged periods. This rebound effect worsens nasal congestion when the drug is discontinued, creating a cycle of dependency.
2. **Headache Medications**: Overuse of pain relievers like aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen can result in rebound headaches, where headaches occur more frequently after prolonged use of these drugs.
3. **Eye Drops with Tetrahydrozoline**: Eye drops containing tetrahydrozoline can cause “rebound redness” in the eyes, leading to a cycle of increased redness and reliance on the drops for relief.
4. **Skin Creams with Hydrocortisone**: Prolonged use of hydrocortisone creams can result in red skin syndrome, characterized by redness, burning, and itching upon discontinuation of the product.
5. **Lip Balm**: While not physically addictive, overuse of lip balms can lead to behavioral addiction, with individuals feeling the need to apply the product excessively.
6. **Laxatives with Bisacodyl, Senna, or Castor Oil**: Stimulant laxatives can cause physiological dependence if used for extended periods, leading to a loss of natural bowel function.
7. **Nasal Inhalers with Propylhexedrine**: Abusing nasal decongestants like Benzedrex for their stimulant effects can result in serious health issues, including high blood pressure and abnormal heart rhythm.
8. **Cough Drugs with Dextromethorphan (DXM)**: Misuse of cough suppressants containing DXM can lead to hallucinations and psychiatric hospitalization at high doses.
9. **Antidiarrheal Drugs with Loperamide**: Loperamide misuse for euphoria or opioid withdrawal can cause severe side effects, including heart problems and respiratory issues.
10. **Antihistamines with Diphenhydramine**: Diphenhydramine in antihistamines like Benadryl can produce intoxicating effects and potential withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of use.
11. **Decongestants with Pseudoephedrine**: Pseudoephedrine-containing decongestants can be misused for stimulant effects, leading to dependence and adverse health outcomes.
Preventing OTC Medication Addiction
It is crucial to use OTC medications responsibly and as directed to avoid the risk of addiction. If you experience any unexpected symptoms or side effects, contact your healthcare provider for guidance. Remember that Poison Control Centers are available 24/7 for immediate assistance if needed.
By raising awareness about the potential risks of over-the-counter drugs and promoting responsible use, individuals can protect themselves from the dangers of medication misuse and addiction. Stay informed, follow label instructions, and seek professional help if you have concerns about your medication usage.