Understanding MPV and Parvovirus: Key Information and Facts
In recent news, there has been a growing concern about two viruses that have been making headlines – MPV and Parvovirus. These viruses have raised alarms among healthcare professionals and the general public due to their potential impact on human health. In this article, we will delve deeper into what MPV and Parvovirus are, how they affect individuals, and what steps can be taken to prevent and treat these infections.
What is MPV?
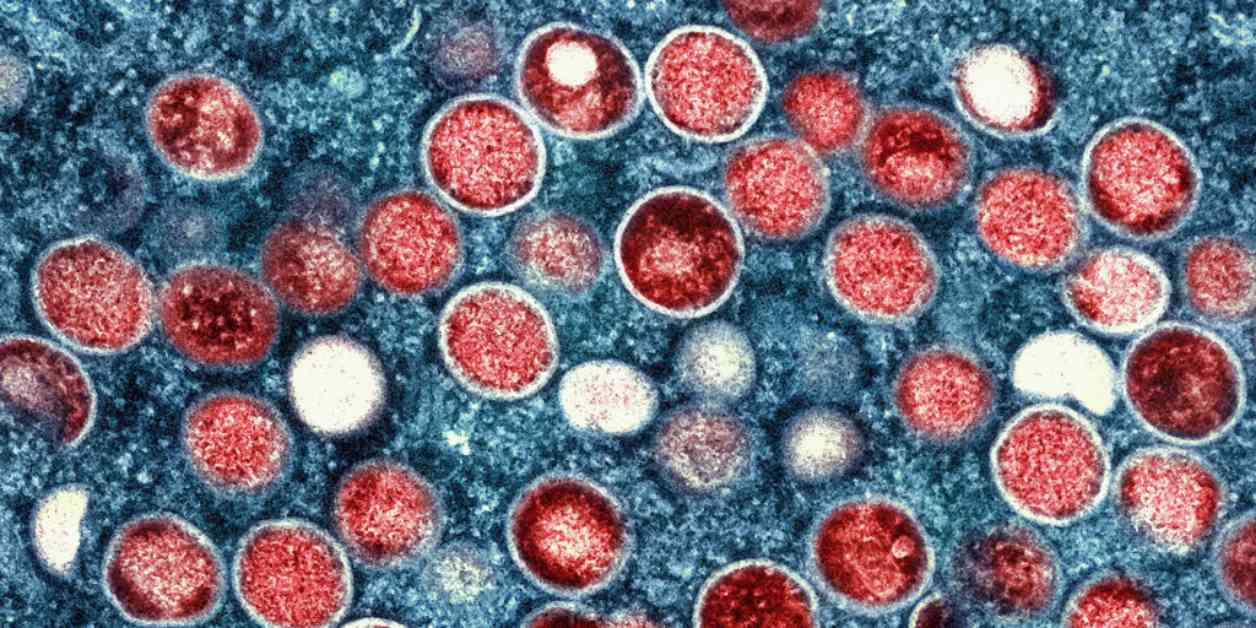
MPV, short for Mammalian Orthopoxvirus, is a virus that primarily affects mammals, including humans. This virus is known to cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild flu-like illness to severe complications. MPV is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets, direct contact with infected individuals, or contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of MPV infection may include fever, fatigue, body aches, and a rash. In severe cases, MPV can lead to pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death. It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you have been infected with MPV to receive proper treatment and prevent the spread of the virus to others.
Understanding Parvovirus
Parvovirus, on the other hand, is a common viral infection that affects humans, particularly children. This virus can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, rash, joint pain, and anemia. Parvovirus is highly contagious and can spread through respiratory secretions, blood transfusions, and mother-to-child transmission.
One of the most concerning aspects of Parvovirus is its potential impact on pregnant women. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has warned of a rise in Parvovirus cases among pregnant women, which can lead to severe complications such as miscarriage or stillbirth. It is crucial for pregnant women to take precautions to avoid Parvovirus infection and seek medical advice if they experience any symptoms.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of MPV and Parvovirus involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and staying home when sick. Vaccination may also be available for certain strains of these viruses, so it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals about vaccination options.
In terms of treatment, there is no specific antiviral medication available for MPV or Parvovirus. Supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms, is often recommended. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and manage complications of the infection.
In conclusion, MPV and Parvovirus are two viruses that pose a risk to human health due to their contagious nature and potential complications. By understanding the symptoms, transmission routes, and prevention strategies for these viruses, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and others from infection. It is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments regarding MPV and Parvovirus and seek medical attention if you suspect you have been exposed to these viruses.