The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has announced a new initiative aimed at reducing the sodium content in packaged and processed foods by about 20% over the next three years. This move comes as part of the agency’s ongoing efforts to address the growing epidemic of diet-related chronic diseases, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
The Importance of Reducing Sodium Intake
Excessive consumption of sodium, commonly found in processed and packaged foods, has been linked to a variety of health issues. High blood pressure, in particular, is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. By lowering the amount of salt in our diets, the FDA hopes to significantly decrease the prevalence of these conditions and improve overall public health.
According to FDA Deputy Commissioner for Human Foods Jim Jones, “Reducing sodium in the food supply has the potential to be one of the most important public health initiatives in a generation.” This sentiment underscores the significance of the agency’s latest initiative and the impact it could have on the well-being of the population.
New Goals and Guidelines
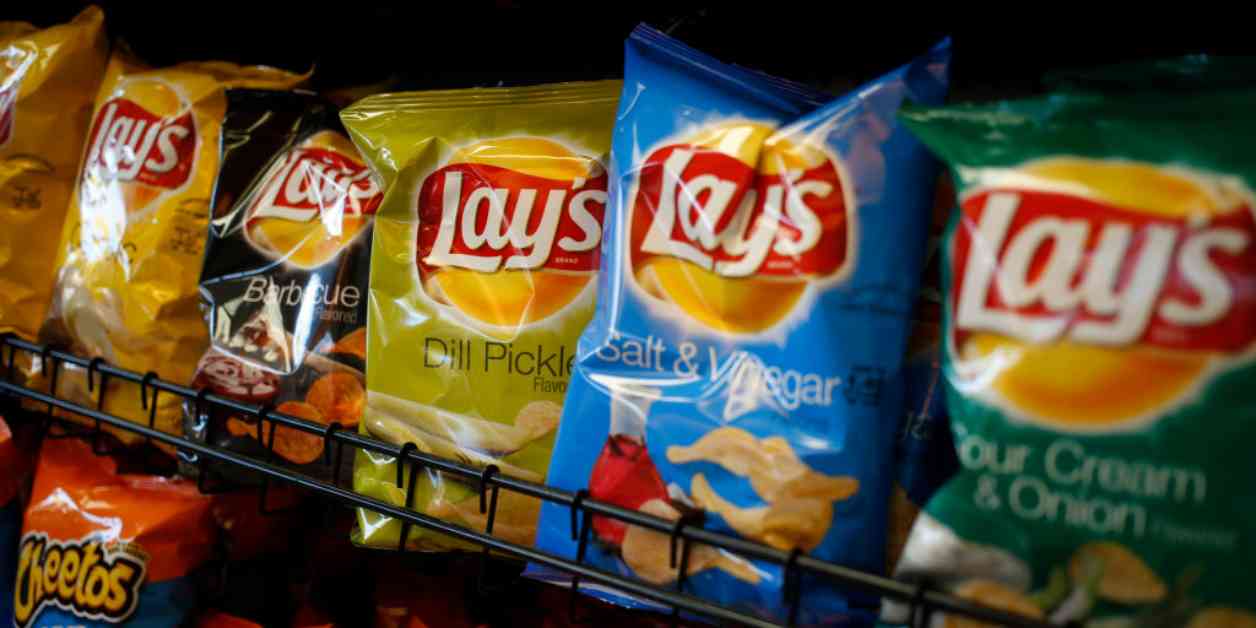
In October 2021, the FDA set guidelines to reduce sodium levels in a wide range of foods, including popular items like potato chips and hamburgers. These guidelines were put in place to address the overconsumption of salt and its detrimental effects on health. Now, the agency is calling on packaged-food manufacturers, such as PepsiCo, Kraft Heinz, and Campbell Soup, to voluntarily decrease the sodium content in their products by 20%.
The FDA aims to lower sodium intake to an average of 2,750 milligrams per day over the next three years. While this target is still above the recommended daily limit of 2,300 mg, it represents a significant step towards reducing the overall salt intake of the population. By working with food manufacturers to implement these changes, the FDA hopes to make a positive impact on public health.
Industry Response and Challenges
As the FDA rolls out its new sodium reduction goals, the response from the food industry remains uncertain. Companies like PepsiCo, Kraft Heinz, and Campbell Soup have yet to comment on the agency’s latest initiative. However, given the potential health benefits of reducing sodium levels in packaged foods, it is likely that these companies will be compelled to comply with the FDA’s guidelines.
Fast-food chains, including industry giants like McDonald’s, Burger King, and Taco Bell, are also expected to be affected by the FDA’s sodium reduction efforts. These establishments serve a significant portion of the population, making it crucial for them to participate in the initiative to lower salt content in their menu items. While these changes may present challenges for the food industry, they also represent an opportunity to promote healthier eating habits among consumers.
Progress and Future Outlook
The FDA has reported that 40% of food categories have already achieved the initial sodium reduction targets set in 2021. This progress indicates that food manufacturers are capable of making significant changes to the sodium content of their products. By continuing to work towards the new 20% reduction goal, the FDA hopes to further improve the nutritional quality of packaged and processed foods available to consumers.
Looking ahead, the success of the FDA’s sodium reduction initiative will depend on the collaboration of food manufacturers, fast-food chains, and other stakeholders in the industry. By working together to promote healthier eating habits and reduce salt intake, these entities can help combat the prevalence of diet-related chronic diseases and improve the overall well-being of the population.
In conclusion, the FDA’s initiative to reduce sodium in packaged and processed foods by 20% represents a significant step towards improving public health. By setting new goals and guidelines for food manufacturers and fast-food chains, the agency aims to lower salt intake and mitigate the risk of conditions like high blood pressure and heart disease. With continued collaboration and effort, this initiative has the potential to make a lasting impact on the health and well-being of the population.