Understanding the Global Emergency of Mpox and Future Implications
The world is once again facing a significant health crisis as the virus known as mpox continues to evolve and spread rapidly. The World Health Organization (W.H.O.) has declared a global health emergency in response to the escalating crisis, marking the first such declaration since the 2022 outbreak of the disease when it was still referred to as monkeypox.
The latest version of the virus has shown a concerning trend of spreading more often through heterosexual populations, a shift from the previous outbreaks primarily affecting gay and bisexual men. This change in transmission patterns has raised alarms among health experts, as it indicates a potentially broader impact on global populations.
Sweden recently reported the first case of mpox outside of Africa, signaling the virus’s ability to travel beyond its initial epicenter. The infected individual had traveled to the African continent, highlighting the interconnected nature of global health and the need for coordinated efforts to combat the spread of infectious diseases.
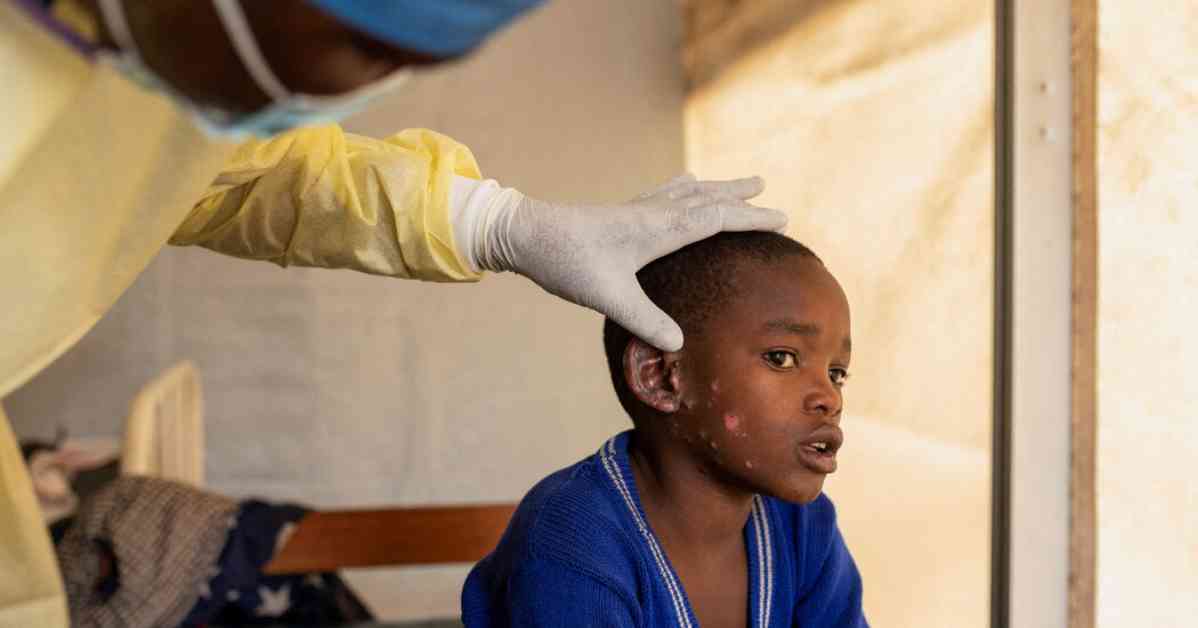
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, where the crisis is most concentrated, the number of mpox cases has been steadily rising. The virus has also spread to a dozen other African countries, posing a significant threat to public health in the region. Experts warn that if the outbreak is not contained, mpox could once again become a global pandemic, with far-reaching implications for communities worldwide.
Implications for Public Health
The escalating crisis of mpox in Africa has raised concerns about the effectiveness of current public health measures in controlling the spread of infectious diseases. With the virus showing a higher propensity for transmission among heterosexual populations, traditional prevention strategies may need to be reassessed to address the evolving nature of the outbreak.
The high number of cases reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo, particularly among children under 15, points to a shift in the disease’s demographics and mode of transmission. This shift could have significant implications for vaccination strategies and outbreak response efforts, requiring a more targeted and proactive approach to containment.
Global Response and Collaboration
In response to the growing threat of mpox, the W.H.O. has called for a concerted effort by all stakeholders to address the crisis effectively. Dr. Dimie Ogoina, a Nigerian scientist and chair of the W.H.O.’s mpox emergency committee, emphasized the need for collaboration not only in Africa but also globally to prevent the further spread of the virus.
The recent case reported in Sweden serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of global health and the importance of international cooperation in combating infectious diseases. As the virus continues to evolve and spread, it is essential for countries to work together to share information, resources, and expertise to mitigate the impact of the outbreak.
As the situation continues to unfold, it is crucial for governments, public health agencies, and communities to remain vigilant and proactive in their response to the mpox crisis. By prioritizing collaboration, communication, and evidence-based interventions, we can work together to contain the spread of the virus and prevent a global pandemic.