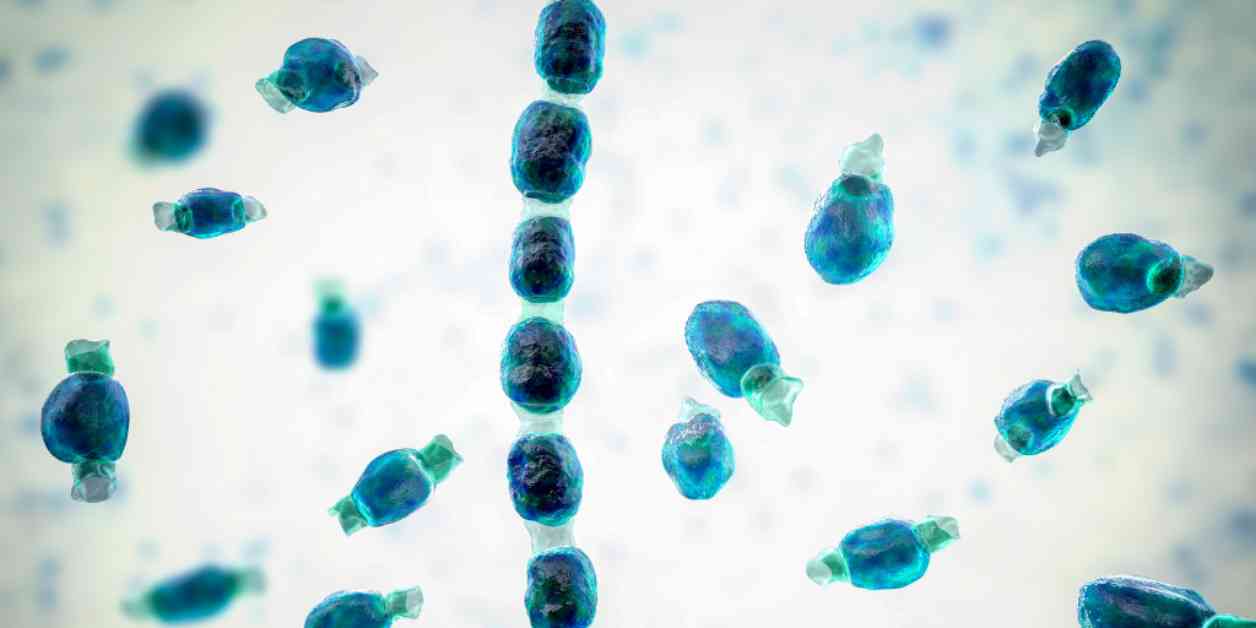
An outbreak of Valley fever among attendees and workers at an outdoor music festival in California’s Central Valley highlights the mounting threat of this fungal infection. Climate change is creating more opportunities for the coccidioides fungus, which causes Valley fever, to proliferate, leading to an increase in cases in recent years.
The recent Lightning in a Bottle Festival in Bakersfield saw 14 individuals test positive for Valley fever, with at least three requiring hospitalization. One such individual, Eric Mattson, described experiencing severe symptoms like body aches, fevers, joint pain, and night sweats after attending the festival. Mattson’s experience underscores the debilitating effects of the infection, which can be confused with pneumonia by healthcare providers.
Valley fever is primarily contracted by inhaling fungal spores present in dust or soil, rather than through person-to-person contact. Symptoms can range from coughing, fatigue, and fever to more severe complications in vulnerable populations, such as those with weakened immune systems. Misdiagnosis is common, as many doctors may not be familiar with the illness or mistake it for another respiratory condition.
The festival’s location in a region where Valley fever is endemic, combined with dusty conditions exacerbated by activities like dancing and camping, created an ideal environment for the fungus to spread. As climate change continues to impact weather patterns, the potential for Valley fever cases to expand beyond traditional endemic regions like California and Arizona is a growing concern.
Studies have suggested that rodents may play a role in spreading the coccidioides fungus, particularly as their migration patterns shift due to environmental changes. Increased awareness among the public about Valley fever and its symptoms is crucial, as early detection and treatment can prevent severe complications and unnecessary antibiotic use.
Moving forward, public health efforts should focus on educating individuals in high-risk areas about the risks of Valley fever and the importance of seeking medical attention if they experience symptoms. By raising awareness and promoting proactive testing, communities can work together to mitigate the impact of this fungal infection and safeguard public health.