ADHD Medication and Psychosis Risk: Understanding the Connection
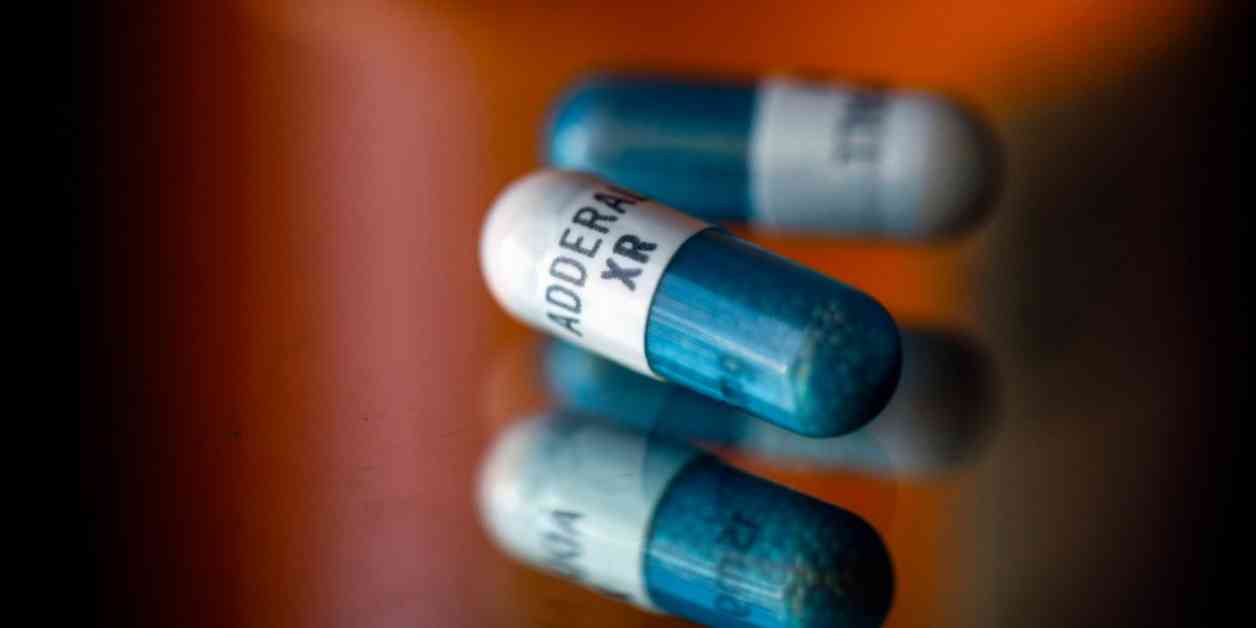
Taking a high dose of ADHD drugs has been found to be linked to a significantly greater risk of developing psychosis or mania, according to a recent study published in the American Journal of Psychiatry. This study sheds light on the potential dangers associated with escalating doses of amphetamines, such as Adderall, Vyvanse, and generic amphetamines like dextroamphetamine, and their impact on mental health.
The Connection Between Amphetamines and Psychosis
Amphetamines are known to increase levels of dopamine in the brain, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including memory, motivation, and mood. However, high levels of dopamine have also been linked to the development of psychotic symptoms. Dr. Jacob Ballon, a psychiatrist at Stanford Medicine, explains, “Amphetamines can flood the brain with dopamine, potentially leading to psychosis.”
What sets this study apart is the establishment of a clear “dose-response relationship,” indicating that the risk of psychosis increases with higher doses of amphetamines. Dr. Will Cronenwett, from Northwestern Medicine, emphasizes the significance of this finding, stating, “This study provides evidence that the risk of psychosis rises as the dosage of ADHD medication escalates.”
The Growing Popularity of Amphetamines in the United States
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of stimulant medications, particularly among adults. A study published in JAMA Psychiatry revealed a 30% rise in prescription rates for amphetamines for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in individuals aged 20 to 39 from 2018 to 2022. Additionally, rates rose by 17% among those aged 40 to 59.
Dr. Moran’s Study on Psychosis Risk
Dr. Lauren Moran, a psychiatrist and researcher at McLean Hospital in Boston, led a study that examined electronic health records from Mass General Brigham between 2005 and 2019. The study focused on teenagers and adults aged 16 to 35, the typical age range for the onset of psychosis or schizophrenia. The researchers identified 1,374 cases of patients hospitalized with first episodes of psychosis or mania, comparing them with 2,748 patients hospitalized for other psychiatric conditions.
The study looked at whether the patients had been prescribed stimulant medications in the past month and analyzed the dosages. Patients taking the highest dosages of amphetamines were found to be 5.3 times more likely to develop psychosis than those not taking stimulants. Similarly, those on medium dosages had a 3.5 times higher risk. It remains unclear whether lower dosages of amphetamines are associated with an increased risk of psychosis.
Amphetamines and Psychosis Risk: A Cautionary Tale
While the risk of developing psychosis from amphetamines remains relatively rare (approximately 1 in 1,000), individuals taking high doses should be aware of the potential dangers. Dr. Cronenwett advises caution, particularly for patients with a personal or family history of serious mental illnesses like bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. He stresses the importance of monitoring medication usage and dosage in these cases.
Dr. Ballon echoes this sentiment, emphasizing the need for patients to be vigilant about the effectiveness of their medication. For some individuals, higher doses may be sought to achieve the desired results, inadvertently increasing the risk of psychosis. It is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to closely monitor dosage levels and be aware of the potential consequences.
Understanding the Risks of ADHD Medication
The study’s findings underscore the importance of informed decision-making when it comes to ADHD medication. Patients and healthcare providers must carefully weigh the benefits of these medications against the potential risks, particularly in cases where high doses are being considered. It is essential for individuals to be proactive in discussing their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Implications for Pharmaceutical Companies
In response to the study, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, the maker of Vyvanse, emphasized the importance of following FDA-approved labeling guidance and consulting with healthcare providers when taking their medications. However, Teva Pharmaceuticals, the manufacturer of Adderall, did not provide a comment on the study’s findings.
Moving Forward: Educating Patients and Healthcare Providers
As the use of amphetamines continues to rise, it is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to be well-informed about the potential risks associated with these medications. Education and awareness can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options and minimize the likelihood of adverse effects.
In conclusion, the link between high doses of ADHD medication and an increased risk of psychosis is a concerning finding that warrants further attention. By understanding the potential dangers associated with these medications and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks, patients and healthcare providers can work together to ensure safe and effective treatment for individuals with ADHD.