Understanding the Mpox Outbreak: Public Health Emergency and Increased Virus Risk in Africa
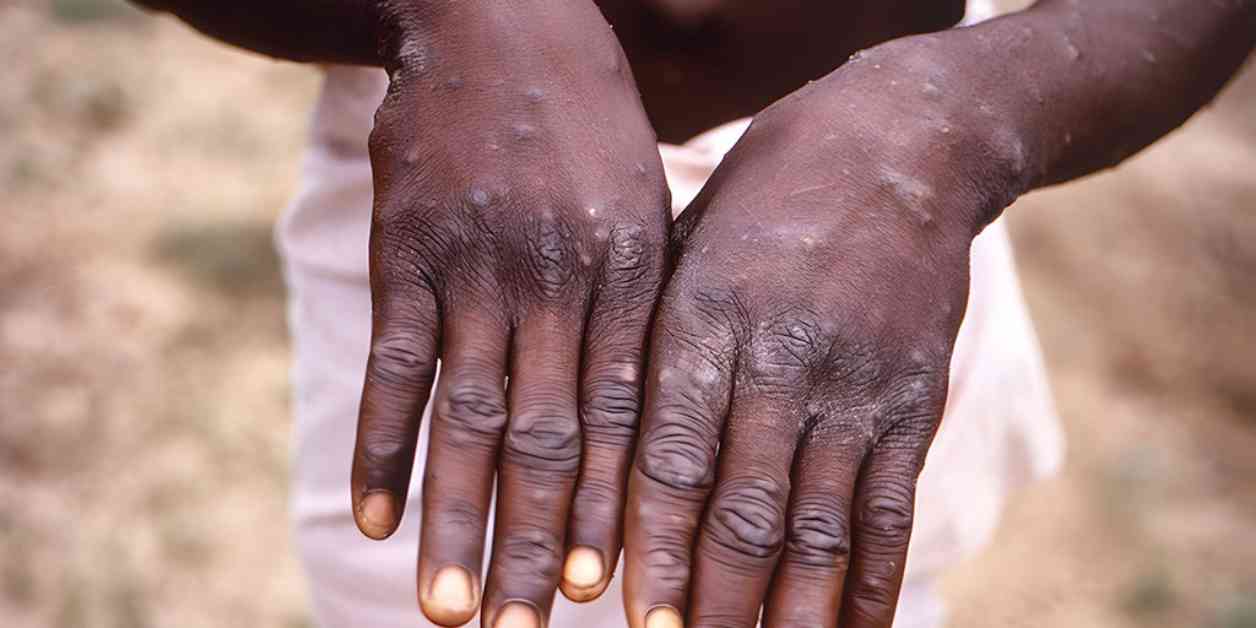
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, has been declared a public health emergency by the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The outbreak has been spreading rapidly throughout the continent, with the African agency reporting a significant increase in cases. There are growing concerns that the virus could potentially cross international borders, posing a threat to global health security.
The Africa CDC has confirmed a 160% increase in overall cases and a 19% rise in deaths compared to the previous year. The majority of mpox cases and fatalities have been reported in Congo, with more than 96% of all cases occurring in the country. Despite this concentration, mpox has been detected in 13 African nations, highlighting the urgent need for coordinated efforts to contain the outbreak.
New Variants and Increased Risks
Recent developments in the outbreak have revealed the emergence of new variants of mpox, raising concerns among health authorities and scientists. A more infectious strain of the virus has been identified in Congo, which has the potential to cause more severe symptoms and increase transmission rates. Unlike traditional mpox, which typically manifests with lesions on the chest, hands, and feet, this new strain presents with milder symptoms and lesions on the genitalia, making it harder to diagnose.
The shift in demographics affected by mpox in Africa is also noteworthy. While the 2022 epidemic primarily impacted gay and bisexual men through close contact, recent patterns show that children under 15 years old account for more than 70% of cases and 85% of deaths in Congo. The reasons behind this disproportionate impact on children remain unclear, with experts speculating about factors such as increased susceptibility, overcrowding, or exposure to infected parents.
International Concerns and Response
The spread of mpox beyond Africa has also become a cause for concern, with Swedish health authorities confirming the first case of the virus in the country. The global implications of the outbreak have prompted discussions about declaring mpox a global health emergency by the World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO Director-General, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, has convened with independent experts to assess the situation and determine the appropriate response.
To support the mpox response in Africa, the WHO has released $1.45 million from its emergency fund. Congo has initiated discussions with donors to secure vaccine donations and has received financial aid from countries like Britain and the U.S. These collaborative efforts are crucial in containing the outbreak and preventing further spread of the virus.
Preventive Measures and Vaccination
As the mpox outbreak continues to escalate, public awareness and preventive measures play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of the virus. The CDC recommends avoiding close contact with individuals displaying mpox symptoms or animals that may carry the virus. Additionally, practicing safe hygiene, especially in social gatherings and sexual encounters, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
For individuals at higher risk of severe mpox infection, such as those with weakened immune systems or pregnant women, vaccination is recommended. The JYNNEOS vaccine, which provides protection against mpox and smallpox, is available as a two-dose regimen. Vaccination is particularly important for individuals with known exposure to mpox cases or those in high-risk scenarios.
The Role of Public Health Education
Public education and awareness campaigns are essential in combating the mpox outbreak and ensuring that individuals are informed about the risks and preventive measures. Health authorities emphasize the importance of early detection, prompt treatment, and proper hygiene practices to limit the spread of the virus. By staying informed and following recommended guidelines, the public can contribute to efforts to contain the outbreak and protect vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, the mpox outbreak in Africa presents a significant public health challenge that requires coordinated efforts at the national and international levels. The emergence of new variants and changing demographics affected by the virus underscore the need for adaptive strategies and targeted interventions. By prioritizing vaccination, preventive measures, and public health education, we can effectively combat the spread of mpox and safeguard global health security.