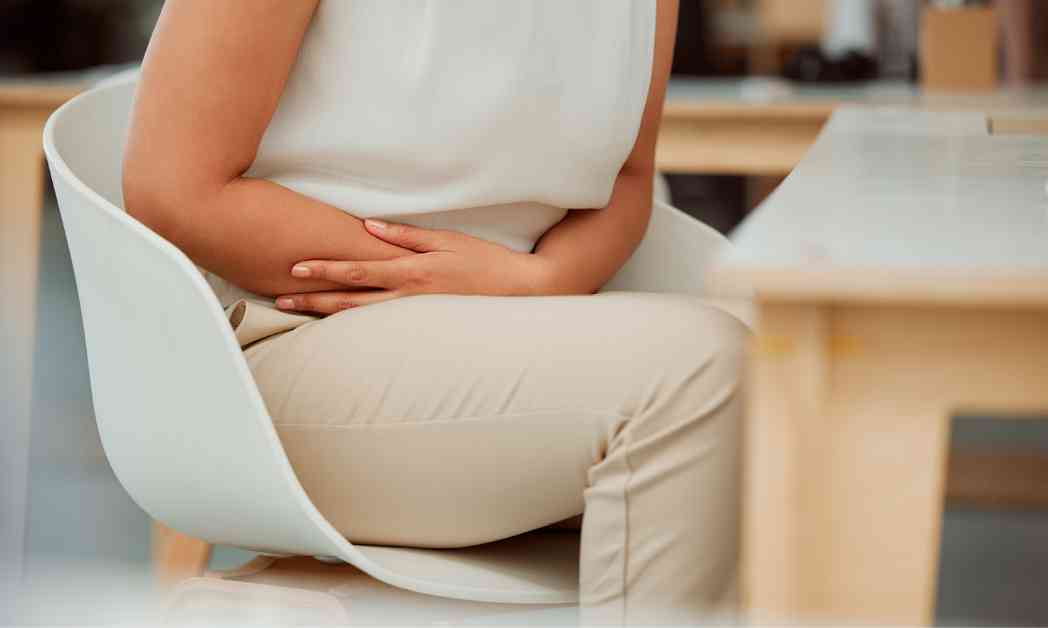
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a condition that causes abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements. Symptoms may include constipation, diarrhea, bloating, and mucus in the stool. It affects the digestive tract but does not cause damage or disease. IBS can vary from person to person, with symptoms coming and going.
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it is considered a functional gastrointestinal disorder. Factors such as sensitivity in the gut and muscle contractions in the bowel may play a role. Around 12% of people in the United States have IBS, with women being affected more than men. Risk factors for IBS include a family history of the condition, stressful life events, mental disorders, bacterial infections, and food sensitivities.
Diagnosing IBS involves ruling out other conditions through tests and exams. Doctors may order blood tests, stool tests, and procedures like sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy. IBS often coexists with other conditions like chronic pain, fibromyalgia, and indigestion.
Treatment for IBS focuses on managing symptoms through diet changes, stress management, and medications for diarrhea or constipation. Probiotics, which are live microorganisms with health benefits, may be recommended. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are specialized plant fibers that nourish good bacteria in the colon. Dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake or following a low FODMAP diet, can also help alleviate symptoms.
Physical activity, sufficient sleep, and mental health therapies are important for managing IBS. Medications are available to treat specific symptoms like stomach pain or diarrhea. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any treatment. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health offers information on alternative treatments like acupuncture and hypnotherapy for IBS.
Overall, IBS is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for IBS, individuals can better navigate and cope with this gastrointestinal disorder.